Approvals
TETStech different models of PTM Charge Ports will all be from the world renowned manufacturers bearing all the Globally recognized Certifications, to ensure its customers a reliable and trust worthy products / services.
The product certifications would include :
- ENERGY STAR® certification – From Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
- UL Listing – OSHA-accredited Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL)
- CE, or Conformité Européene – conformity with health, safety, and EPA standards
- RoHS – Restriction of Hazardous Substances
PTM Charge Ports from TETStech would cover all the above Global standards and will be from Certified manufacturers meeting all the NEC (National Electrical Codes


STANDARDS of Charging Ports
TETStech network of PTM (POWER TELLER MACHINES) will have the Global Standards of Charging Ports which are approved by the Ministry of Power (MoP), Government of India for the public & private (residential) utilities.
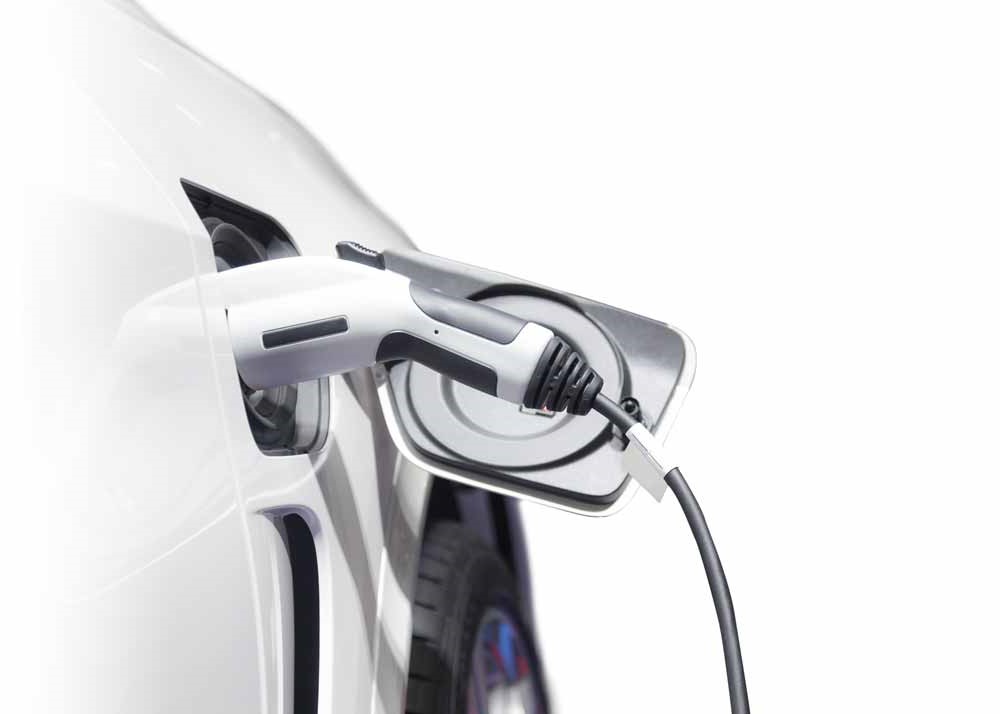
Communication between the power source and the vehicle’s battery and on-board charger is critical to ensure the safety of the user and the longevity of the battery and the charging connectors. Allowing the vehicle to detect when the plug is fully inserted allows the on-board charger and supply equipment to ensure that both sides of the connection are always safe to touch. The vehicle must detect when the latch is pressed on the connector to allow the vehicle to stop drawing power before the connector is unplugged to prevent arcing.
The vehicle must be able to communicate what voltages and currents it can accept and whether ventilation is required to prevent overheating. Additionally, the supply equipment must constantly monitor for ground faults to ensure that the vehicle’s chassis remains isolated from the battery.
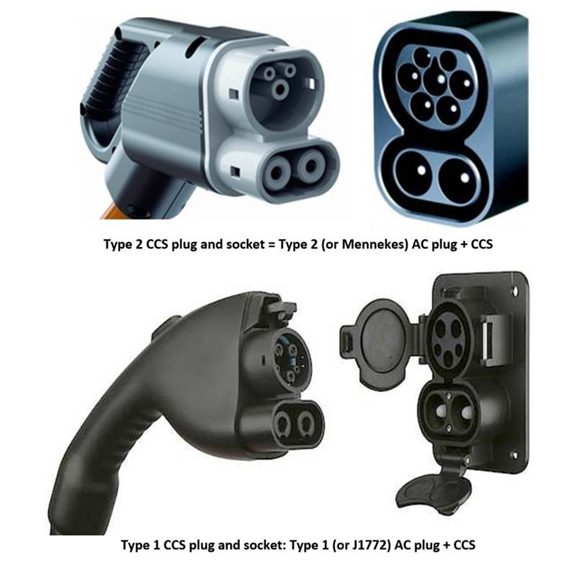
1. CCS (Combined Charging System)
These charging sockets combine the inlets for both AC and DC using shared communication pins. CCS1 and CCS2 share the design of the DC pins as well as the communications protocols. These are widely used in Americas & Europe.
CCS1 and CCS2 share the design of the DC pins as well as the communications protocols, therefore it is a simple option for manufacturers to swap the AC plug section for Type 1 in the US and (potentially) Japan for Type 2 for other markets.
It is worth noting that to initiate and control charging, CCS uses PLC (Power Line Communication) as the communication method with the car, which is the system used for power grid communications.
This makes it easy for the vehicle to communicate with the grid as a ‘smart appliance’.
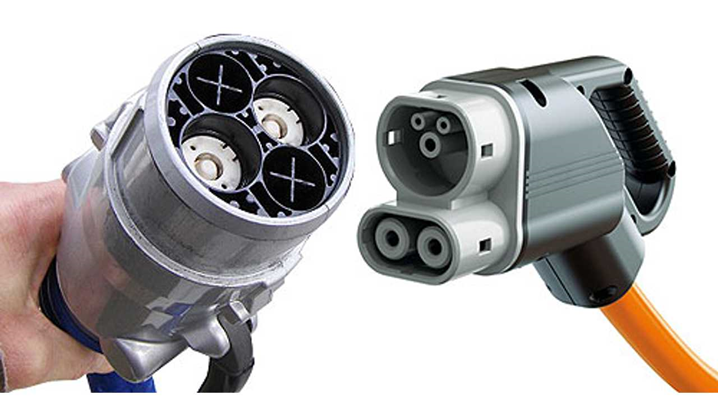


2. CHAdeMO standards – Invented & Introduced by Japan.
These charging sockets combine the inlets for both AC and DC using shared communication pins. CCS1 and CCS2 share the design of the DC pins as well as the communications protocols. These are widely used in Americas & Europe.
CCS1 and CCS2 share the design of the DC pins as well as the communications protocols, therefore it is a simple option for manufacturers to swap the AC plug section for Type 1 in the US and (potentially) Japan for Type 2 for other markets.
It is worth noting that to initiate and control charging, CCS uses PLC (Power Line Communication) as the communication method with the car, which is the system used for power grid communications.
This makes it easy for the vehicle to communicate with the grid as a ‘smart appliance’.
3. Bharat AC 001 and Bharat DC 001
An EVSE supplies AC current to the vehicle’s onboard charger which in turn converts the AC power to DC allowing the battery to be charged.
Normal AC charging
As mentioned above, electric 2-wheelers, 3-wheelers and 4-wheeler vehicles in India has on-board charger that charge at rate of around 2.5kW to 3kW.
These AC 2.5KW or 3KW Chargers could fast charge a 2-wheeler (for a battery with an energy density of 2KWh) in an hour’s time; 4-wheeler or larger vehicles with batteries of 12 KWh or more will be charged in five to six hours.
Fast AC charging
Global electric cars like the Nissan Leaf or the Tesla have on board chargers with higher power ratings. This enables AC charging at a faster rate, from 7.7 kw to 22 kw.
DC Fast Charging
In this method of charging, DC current is sent to the electric car’s battery directly via the DC charge port. Fast charging’s faster charge rate (usually 50 kiloWatts or more outside India) can supply 100 or more km’s of range per hour of charging. A significant fast charging network available should make electric cars more attractive than otherwise, and lead to higher adoption rates.
Level 1 DC Chargers
Public DC Chargers at output voltage of 48V / 72V, with power outputs of 10 kW / 15 kW with maximum current of up to 200A.As per the Bharat EV specs, these will be called Level 1 DC Chargers.
Level 2 DC Chargers
Public DC Chargers at output voltage up to 1000V, with power outputs of 30 kW / 150 kW. These will be called Level 2 DC Chargers.